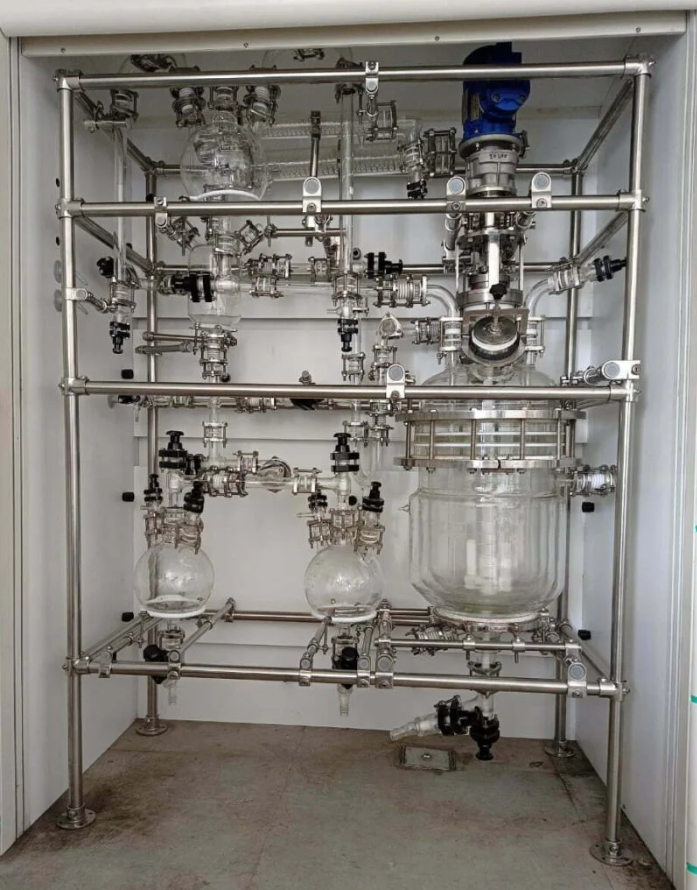
Introduction
Moving from laboratory research to full-scale production is crucial in the pharmaceutical and chemical industries. This transition requires careful planning, testing, and evaluation to ensure efficiency and safety. This is where pilot plants play a vital role. These small-scale production units help bridge the gap between research and large-scale manufacturing, optimizing. processes before full-scale deployment.
What are Pilot Plants?
A pilot plant is a small, intermediate version of an industrial production facility. It allows companies to test, refine, and validate processes before committing to full-scale manufacturing. Pilot plants are commonly used in the pharmaceutical, chemical, and other process industries to scale up from laboratory experiments while addressing potential challenges in production.
Importance of Pilot Plants in Pharmaceutical & Chemical Industries
1. Process Optimization
One of the primary reasons for using a pilot plant is to fine-tune the manufacturing process. Before scaling up production, it is essential to optimize factors like temperature, pressure, mixing, and reaction time. A well-designed pilot plant helps engineers and scientists make necessary adjustments to improve efficiency and product quality.
2. Cost Reduction
Investing in a pilot plant can significantly reduce production costs in the long run. Instead of risking large-scale failures, companies can identify inefficiencies and rectify them in the pilot phase. This prevents costly errors in full-scale manufacturing, saving both time and resources.
3. Product Quality & Consistency
In industries like pharmaceuticals, product quality and consistency are non-negotiable. A pilot plant helps manufacturers ensure that the production process consistently yields high-quality products. It also helps in meeting regulatory standards by providing reliable data on product stability, purity, and effectiveness.
4. Regulatory Compliance and Safety Testing
Government regulations in the pharmaceutical and chemical industries are strict. A pilot plant allows companies to test their processes and products under real-world conditions to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. This includes evaluating environmental impact, worker safety, and adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
5. Risk Mitigation
Scaling up a new chemical or pharmaceutical product without thorough testing can be risky. A pilot plant minimizes these risks by identifying potential issues early in the development process. Whether it is equipment failure, raw material variability, or unexpected reactions, a pilot plant allows companies to address these challenges before full-scale production.
6. Process Scale-Up & Technology Transfer
The transition from laboratory research to commercial production involves process scale-up and technology transfer. A pilot plant helps bridge this gap by replicating lab conditions on a larger scale while identifying challenges that may arise. This ensures a smooth transfer of technology and knowledge to full-scale operations.
7. Testing New Equipment & Technologies
With continuous advancements in process technology, industries must adopt new equipment and techniques to remain competitive. A pilot plant provides a platform to test and validate new technologies before integrating them into large-scale production. This helps in innovation while minimizing operational risks.
8. Environmental & Sustainability Considerations
The chemical and pharmaceutical industries are increasingly focusing on sustainable practices. A pilot plant helps evaluate the environmental impact of processes, optimize resource utilization, and develop eco-friendly manufacturing techniques. This is crucial for minimizing waste and reducing the carbon footprint of industrial processes.
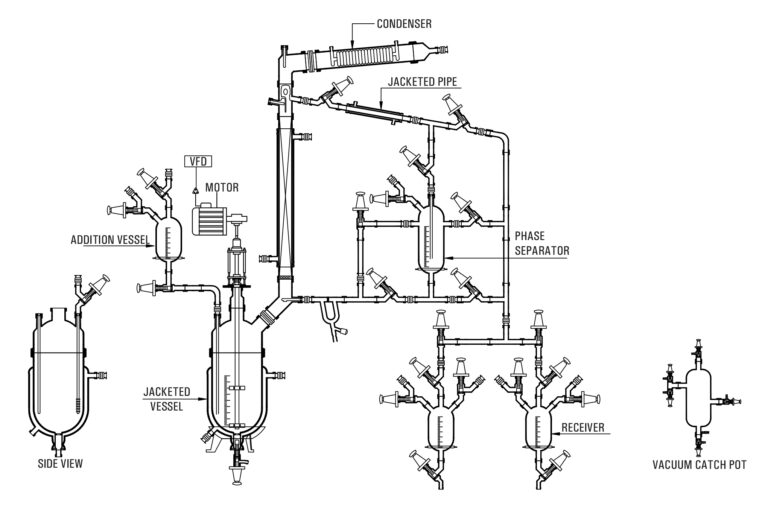
Applications of Pilot Plants in the Pharmaceutical & Chemical Industries
Pharmaceutical Industry Applications
- Drug Development & Formulation: Testing new drug formulations and optimizing production techniques.
- API (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient) Production: Scaling up API manufacturing while ensuring consistency.
- Biopharmaceuticals & Biotechnology: Testing bioreactors, fermentation processes, and purification methods.
- Quality Control & Stability Testing: Ensuring that pharmaceutical products meet required standards before mass production.
Chemical Industry Applications
- Chemical Synthesis & Reaction Engineering: Developing and testing chemical synthesis methods.
- Polymer & Material Science: Producing and testing new polymer materials and coatings.
- Catalyst Testing & Development: Evaluating the efficiency of catalysts in industrial reactions.
- Process Safety & Hazard Analysis: Identifying potential hazards and implementing safety measures.
Choosing the Right Pilot Plant
When setting up a pilot plant, industries must consider factors such as:
- Process Requirements: The pilot plant should closely mimic the intended full-scale production conditions.
- Flexibility & Scalability: The design should allow modifications and easy scale-up.
- Regulatory Compliance: The facility must adhere to industry-specific regulations and safety standards.
- Investment & Operational Costs: Balancing cost-effectiveness while maintaining quality and safety.
Conclusion
In both pharmaceutical and chemical industries, pilot plants play a crucial role in ensuring a smooth transition from laboratory research to full-scale production. They help optimize processes, reduce costs, enhance product quality, and mitigate risks. By investing in pilot plants, companies can achieve efficient, safe, and compliant production processes.
For high-quality pilot plant solutions, trust Goel Impex for reliable and efficient industrial glassware and process equipment customized to your needs.






